Attribute Routing With ASP.net MVC 5
简介
- 本文介绍在应用程序中使用 ASP.net MVC 5 Attribute Routing 最新特性;
- 本文分两部分, 第一部分介绍 Attribute Routing 的基本用法, 第二部分介绍一些高级用法。
什么是 Routing ?
Routing 是 ASP.net MVC 将地址映射为 Action 方法的技术。
什么是 Attribute Routing ?
ASP.net MVC 5 支持一种新类型的路由, 称之为 Attribute Routing 。 顾名思义, Attribute Routing 使用来标记定义路由, Attribute Routing 让你在程序中更好的控制资源地址。
如何启用 Attribute Routing ?
- 要启用 Attribute Routing, 选中并打开
App_Start目录中的RouteConfig.cs; - 如下所示, 调用
MapMvcAttributeRoutes方法。
RouteConfig.cs
public class RouteConfig
{
public static void RegisterRoutes(RouteCollection routes)
{
routes.IgnoreRoute("{resource}.axd/{*pathInfo}");
routes.MapMvcAttributeRoutes();//Attribute Routing
//Convention-based Routing
routes.MapRoute(
name: "Default",
url: "{controller}/{action}/{id}",
defaults: new { controller = "Home", action = "Index",
id = UrlParameter.Optional }
);
}
}
代码要点
- 要启用 Attribute Routing ,必须在
RouteConfig.cs文件中调用MapMvcAttributeRoutes方法; - 如果需要, 可以向上面的代码一样保留基于约定的路由;
- 但是,
routes.MapMvcAttributeRoutes()必须在基于约定的路由之前配置。
如何使用可选 URI 参数 ?
- 在路由参数上添加一个问号
- 对, 就像这样:
[Route("Pet/{petKey?}")]
PetController.cs
public class PetController : Controller
{
// eg: /Pet
// eg: /Pet/123
[Route("Pet/{petKey?}")]
public ActionResult GetPet(string petKey)
{
return View();
}
}
代码要点
- 在上面的例子中,
/Pet和/Pet/123都将被路由到GetPet方法;
上面的路由在浏览器中看起来是这样的:
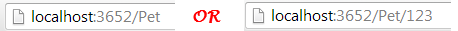
如何使用带默认值的 URI 参数 ?
- 在路由参数中指定默认值;
- 例如:
[Route("Pet/Breed/{petKey=123}")]
PetController.cs
public class PetController : Controller
{
// eg: /Pet/Breed
// eg: /Pet/Breed/528
[Route("Pet/Breed/{petKey=123}")]
public ActionResult GetSpecificPet(string petKey)
{
return View();
}
}
代码要点
- 在上面的例子中,
/Pet/Breed和/Pet/Breed/528都会被路由到GetSpecificPet方法。
上面的路由在浏览器中看起来是这样的:

如何使用路由前缀 ?
- 一般来说, 同一个 Controller 的路由都使用相同的前缀;
- 例如:
/Booking
BookingController.cs
public class BookingController : Controller
{
// eg: /Booking
[Route("Booking")]
public ActionResult Index() { return View(); }
// eg: /Booking/5
[Route("Booking/{bookId}")]
public ActionResult Show(int bookId) { return View(); }
// eg: /Booking/5/Edit
[Route("Booking/{bookId}/Edit")]
public ActionResult Edit(int bookId) { return View(); }
}
上面的路由在浏览器中看起来是这样的:

如何设置公用路由前缀 ?
- 可以根据需要为整个 Controller 指定一个公用的路由前缀;
- 那就需要使用
[RoutePrefix]前缀; - 例如:
[RoutePrefix("Booking")]
BookingController.cs
[RoutePrefix("Booking")]
public class BookingController : Controller
{
// eg: /Booking
[Route]
public ActionResult Index() { return View(); }
// eg: /Booking/5
[Route("{bookId}")]
public ActionResult Show(int bookId) { return View(); }
// eg: /Booking/5/Edit
[Route("{bookId}/Edit")]
public ActionResult Edit(int bookId) { return View(); }
}
上面的路由在浏览器中看起来是这样的:

如何覆盖公用路由前缀 ?
- 可以在标记前面添加一个波浪线 (~) 来覆盖公用前缀;
- 例如:
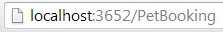
[Route("~/PetBooking")]
BookingController.cs
[RoutePrefix("Booking")]
public class BookingController : Controller
{
// eg: /PetBooking
[Route("~/PetBooking")]
public ActionResult PetBooking() { return View(); }
}
上面的路由在浏览器中看起来是这样的:
如何使用默认路由 ?
- 可以在 Controller 上使用
[Route]标记, 并将 Action 作为参数; - 路由会在所有的 Action 方法中启用;
- 例如:
[Route("{action=index}")]
BookingController.cs
[RoutePrefix("Booking")]
[Route("{action=index}")]
public class BookingController : Controller
{
// eg: /Booking
public ActionResult Index() { return View(); }
// eg: /Booking/Show
public ActionResult Show() { return View(); }
// eg: /Booking/New
public ActionResult New() { return View(); }
}
上面的路由在浏览器中看起来是这样的:

如何覆盖默认路由 ?
- 需要在一个指定的 Action 方法上使用
[Route]标记; - 这样就会覆盖默认设置, 如下所示:
BookingController.cs
[RoutePrefix("Booking")]
[Route("{action=index}")]
public class BookingController : Controller
{
// eg: /Booking
public ActionResult Index() { return View(); }
// eg: /Booking/Edit/3
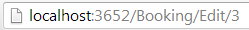
[Route("Edit/{bookId:int}")]
public ActionResult Edit(int bookId) { return View(); }
}
上面的路由在浏览器中看起来是这样的:
如何为路由指定名称 ?
- 可以为路由指定名称, 通过路由名称可以很容易的生成 URI 链接
- 比如这样:
[Route("Booking", Name = "Payments")]
BookingController.cs
public class BookingController : Controller
{
// eg: /Booking
[Route("Booking", Name = "Payments")]
public ActionResult Payments() { return View(); }
}
- 然后可以使用
Url.RouteUrl方法来生成链接; - 就像这样:
<a href="@Url.RouteUrl("Payments")">Payments Screen</a>
注意 : 在上面的代码中, “Payments” 是路由的名称。
相对于传统的基于约定的路由, Attribute Routing 的优点是:
- 在应用中可以更好的控制 URI 资源;
- 容易诊断并解决问题;
- 不用担心修改其中一个路由会影响到其它的路由;
原文地址 (需要翻墙), 还有 Attribute Routing in Web API 2, Create a REST API with Attribute Routing in Web API 2